Botanical Classification of Cacti: An Intriguing Overview
The world of cacti, encompassing a remarkable diversity of forms and adaptations, is a fascinating realm within the plant kingdom. While they are often associated with arid environments and striking geometrical aesthetics, their scientific classification reveals a complex narrative filled with evolutionary ingenuity. The essence of this classification lies in the scientific name, which conveys information about the organism’s taxonomic placement and its relationships with other flora.
Understanding the scientific names of cacti not only enriches our appreciation of these unique plants but also enhances our ability to study and cultivate them effectively. The sheer variety and beauty associated with different cacti species make them a topic of great interest for botanists, horticulturists, and plant enthusiasts alike.
The Science Behind Scientific Classification
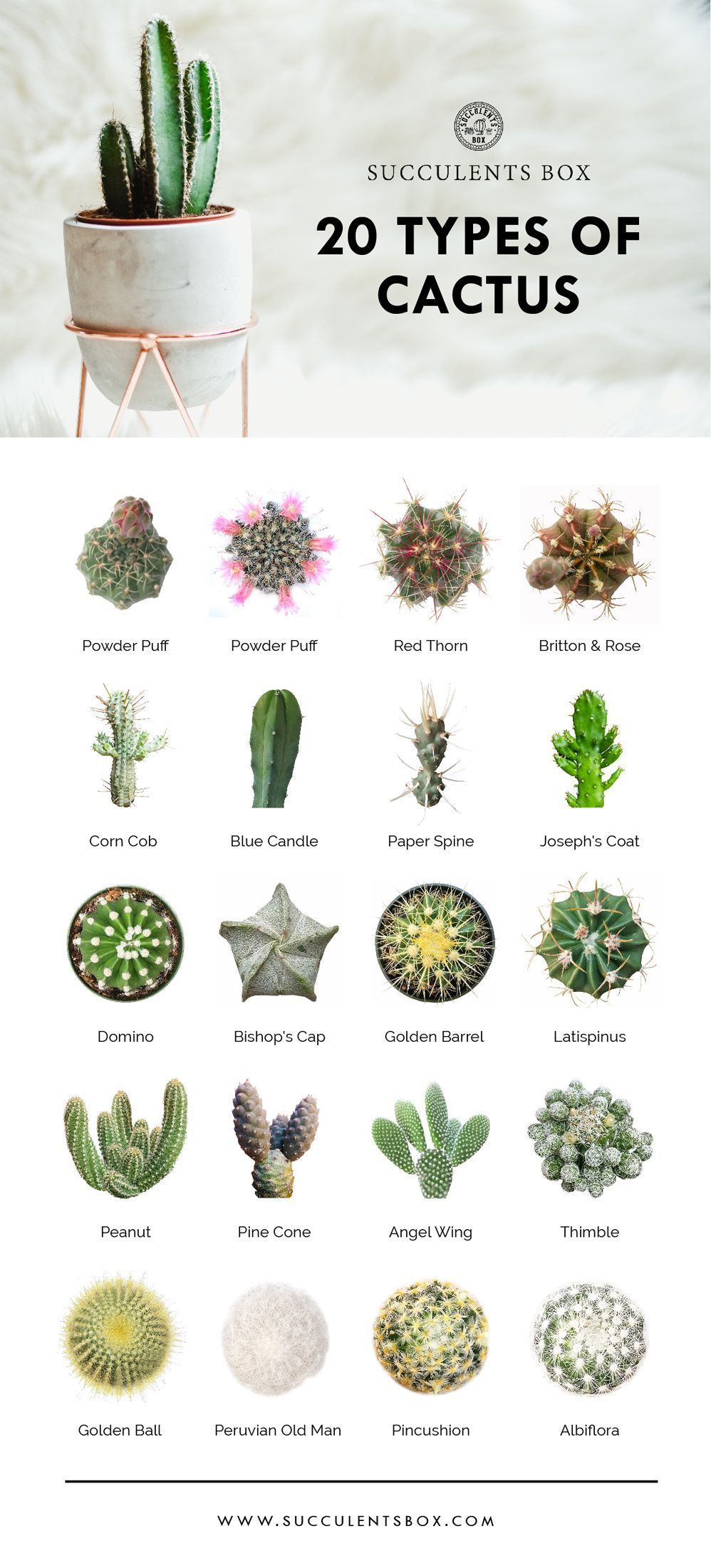
At the foundation of plant classification is a system known as taxonomy. It is an organized method that categorizes living organisms based on shared characteristics. Cacti belong to the family Cactaceae, which is characterized by succulence and the ability to thrive in arid conditions. This family encompasses over 2,000 species, each with its unique adaptations and morphological traits.
The scientific name of a cactus typically follows the binomial nomenclature system, which includes two main components: the genus and the species. For example, in the scientific name Echinocactus grusonii, “Echinocactus” represents the genus, while “grusonii” denotes the species. This method provides a universal naming convention, allowing for efficient communication and identification across different regions and languages.
Delving into the Genus: The Hierarchical Structure
The genus is a crucial element in the classification of cacti. It groups together species that share common features, while also distinguishing them from other genera within the family. Some of the prominent genera within the Cactaceae family include:
1. Echinocactus: Known for its ribbed, spiny appearance, members of this genus are often rounded and can exhibit a vibrant flowering display, particularly during the spring.
2. Opuntia: Commonly known as prickly pears, these cacti are characterized by their flattened pads and are notable for their edible fruit and pads, which are utilized in various culinary traditions.
3. Cereus: This genus includes tall, column-like cacti that can reach impressive heights and produce large, aromatic flowers that bloom at night, attracting various pollinators.
Each genus showcases a unique array of characteristics, from growth patterns to reproductive strategies, contributing to the overall rich tapestry of cactus biodiversity and aesthetics.
Aesthetic Appeal: The Allure of Cacti
The aesthetic appeal of cacti is undeniable. Their fascinating shapes, textures, and colors create striking visual statements in gardens and homes alike. This allure can also be traced back to their scientific classification. Certain genera produce more visually captivating species than others, often capturing the imagination of plant enthusiasts.
For instance, the genus Echinopsis is celebrated for its vibrant flowers, which can vary in color from pink to deep red and even white. Such attributes make these cacti highly desirable for collectors and decorators, transcending their simple survival adaptations and revealing an intricate beauty that is often overlooked in traditional plant studies. This interplay between form and function not only captures attention but also serves as a reminder of nature’s creativity.
Cacti in Ecosystem Dynamics: A Functional Perspective
The unique classification of cacti extends beyond aesthetic appreciation; it also highlights their pivotal roles in ecosystem dynamics. Cacti have evolved various adaptations that allow them to flourish in arid environments, making them essential components of their native habitats.
For example, some cacti store water in their fleshy tissues, enabling them to survive prolonged drought periods. This water storage capability is not only a survival strategy but also a potential resource for wildlife and other plants in times of scarcity. Additionally, cacti are often pivotal in maintaining soil integrity and preventing erosion in desert landscapes.
The pollination interactions that many cacti engage in with insects and birds further illustrate their ecological significance. Many species have evolved specific floral traits to attract particular pollinators, ensuring successful reproduction. The mutualistic relationships forged during these processes enrich the biodiversity of their surroundings, showcasing the interconnectedness of life.
The Future of Cacti: Conservation and Cultivation
As we continue to navigate the challenges of climate change and habitat destruction, the conservation of cactus species becomes increasingly imperative. The unique adaptations that enable these plants to survive in harsh conditions also make them susceptible to extinction due to environmental changes. Understanding proper classification and taxonomy facilitates effective conservation strategies, allowing scientists and conservationists to prioritize efforts based on species diversity and threat levels.
In conjunction with conservation, the cultivation of cacti has found a renewed interest among gardeners and plant lovers. By employing methods that respect the native habitats and typical growth patterns of these plants, cultivators are better equipped to foster a thriving cactus collection. Furthermore, an understanding of scientific names, classifications, and ecological roles enhances their engagement with these iconic plants.
In conclusion, the scientific classification of cacti offers insights into the complex relationships and unique adaptations of these remarkable plants. Their aesthetic appeal and ecological significance intertwine, compelling us to appreciate them not only as decorative elements but as vital components of our planet. The exploration of cacti, from their scientific names to their contributions to ecosystem dynamics, opens a door to deeper understanding and appreciation of the natural world. Embracing this knowledge ultimately paves the way for more mindful interactions with these fascinating flora.



Leave a Comment