Understanding the scientific classification of cacti is essential for both enthusiasts and horticulturists. The cactus family, known for its unique adaptations and diverse forms, has captured the attention of plant lovers worldwide. This article delves into the scientific nomenclature and classification of cacti, revealing the complexities behind their categorization.
The botanical classification of cacti falls under the family Cactaceae, a term derived from the Greek word “kaktos.” This family comprises over 2,000 species spread across approximately 175 genera. Cacti are primarily native to the Americas, with a few species found in tropical regions. The unique morphology of cacti—such as their fleshy stems and spines—leads to their distinct classification and identification within the plant kingdom.
The Taxonomy of Cacti: A Detailed Overview
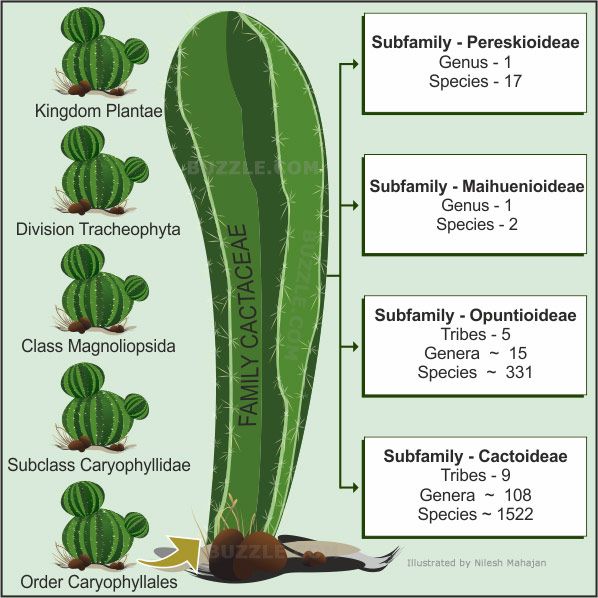
Taxonomy involves the hierarchical classification of organisms into categories. For cacti, this structure begins at the kingdom level and proceeds through a series of ranks down to species. The standard classification of cacti is as follows:
Kingdom: Plantae
Subkingdom: Tracheobionta
Superdivision: Spermatophyta
Division: Angiosperms
Class: Eudicots
Order: Caryophyllales
Family: Cactaceae
Each level within this classification plays an essential role in understanding the relationships among various plants. The family Cactaceae is further divided into subfamilies, tribes, and genera, each showcasing unique characteristics that define their ecological and morphological features.
Exploring the Genera of Cacti
Within the family Cactaceae, cacti are organized into numerous genera. This section examines some of the most notable genera, highlighting their distinctive traits and examples of popular species.
Genus: Opuntia
Opuntia, commonly known as prickly pear, is one of the largest genera within the cactus family. Characterized by its flattened pads and vibrant fruit, the prickly pear is well-adapted to arid environments. Notable species include Opuntia ficus-indica, which is economically significant for its edible fruits.
Genus: Echinocactus
Echinocactus, often referred to as barrel cacti, is distinguished by its globular shape and pronounced ribs. These cacti can grow large and exhibit beautiful flowers that bloom primarily during the summer months. Echinocactus grusonii, also known as the golden barrel cactus, is a popular ornamental choice due to its striking appearance and low maintenance requirements.
Genus: Mammillaria
The genus Mammillaria encompasses small, globose cacti that are often adorned with intricate patterns of tubercles. Mammillaria species are widespread in Mexico and are prized for their stunning floral displays. Mammillaria bocasana, known as the woolly nipple cactus, features a charming fuzzy exterior and vibrant pink flowers.
These genera exemplify the diversity within the cactus family, showcasing a range of physical forms and ecological adaptations. Each genus contains species that are specially adapted to thrive in varying environments, from deserts to rocky slopes.
The Importance of Scientific Names: A Universal Language
Scientific names provide a consistent and universal naming convention, eliminating confusion that arises from common names. The binomial nomenclature is key to this system, where each species is identified by its genus name and a specific epithet. For example, in the case of the classic Saguaro cactus, its scientific name is Carnegiea gigantea.
Understanding these names is crucial for research and conservation. For instance, many cacti are threatened by habitat destruction and climate change. By using precise scientific names, researchers can effectively communicate their findings and devise strategies for preservation.
This standardization plays a vital role in the global discourse on biodiversity, providing a framework for scientists, horticulturists, and conservationists to share knowledge and resources for the protection of these remarkable plants.
Conclusion: The Fascinating World of Cacti
The botanical classification of cacti serves not only as a means of identification but also as a gateway to understanding their evolutionary history and ecological significance. With intricate taxonomy, diverse genera, and the importance of scientific nomenclature, the study of cacti offers endless opportunities for exploration and appreciation. As we continue to learn more about these resilient plants, their classifications will shed light on the myriad ways they interact with their environments and how they can be cultivated and conserved for future generations.



Leave a Comment