Cacti are a fascinating and diverse group of plants recognized for their ability to thrive in arid environments. Understanding the scientific names of cacti unveils not only their identity but also provides insight into their evolutionary history, ecological significance, and relationships with other species. In this article, we delve into the complex world of cactus classification, exploring the nuances of botanical nomenclature, the various families and genera of cacti, and their unique characteristics.
The foundation of plant taxonomy lies in the Linnaean system, developed by Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. This system relies on a hierarchical classification that begins with broader categories and narrows down to specific species. Ultimately, each species is assigned a binomial name comprising the genus and species identifier. The scientific name of a cactus includes this system, which assists botanists and enthusiasts alike in accurately identifying and classifying these remarkable plants.
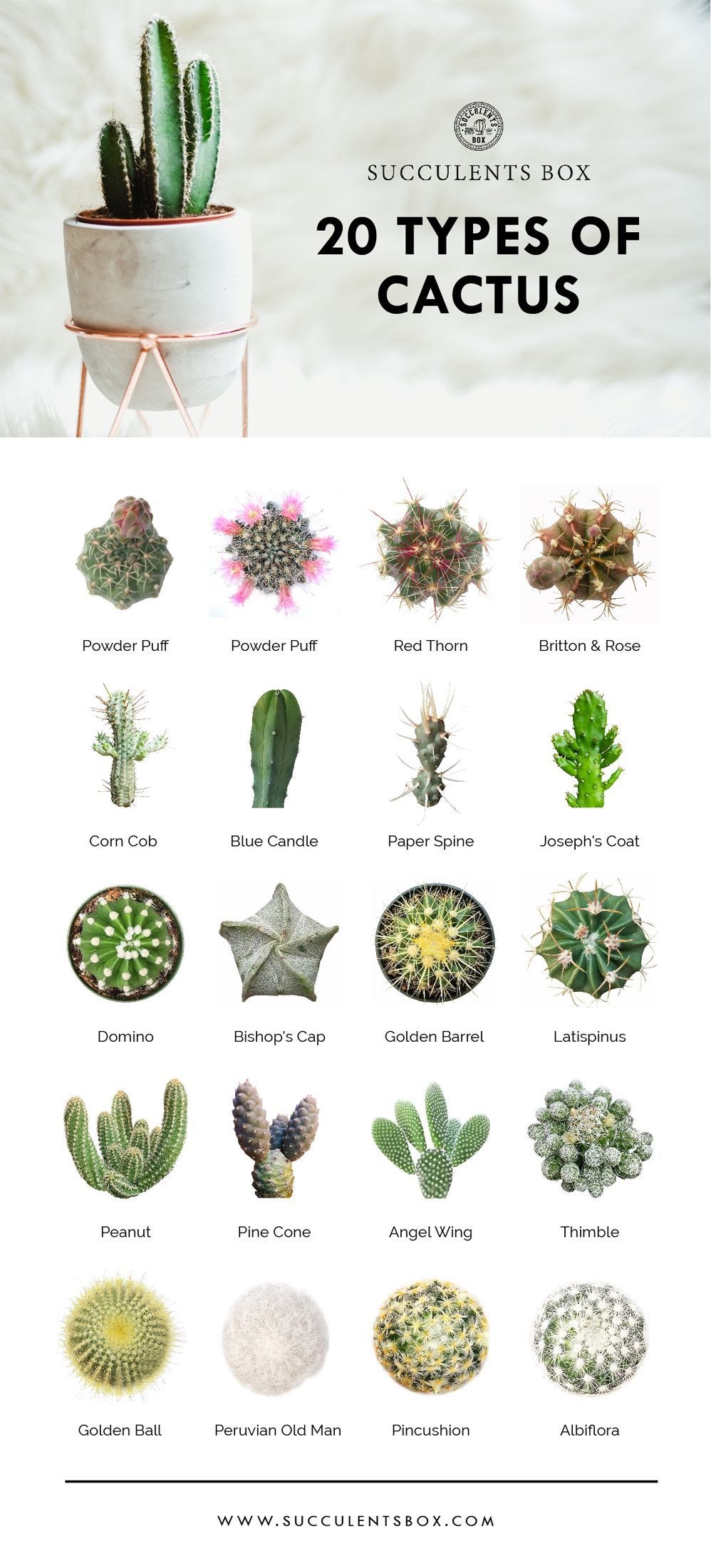
The primary family of cacti is Cactaceae, which encompasses a wide array of genera and species. The adaptations that cacti have developed allow them to survive in desserts, rocky terrains, and other challenging ecosystems. Understanding the scientific names and classification of cacti is essential, not only for horticulturists but also for conservationists and ecologists. The following sections explore the major groups within the Cactaceae family.
One major genus within the cacti family is Opuntia, commonly known as the prickly pear. This genus boasts numerous species characterized by their flat pads and vibrant flowers. Prickly pears are famous not only for their stunning appearance but also for their edible fruit, known as ‘tunas.’ Their scientific name follows the binomial nomenclature, appearing as Opuntia spp. for species under this genus, with specific names such as Opuntia ficus-indica for the widely cultivated species.
Another prominent genus is Carnegiea, which comprises iconic species such as the saguaro cactus. This remarkable plant, scientifically designated as Carnegiea gigantea, can reach heights of up to 40 feet and live for over fifty years. The saguaro cactus is endemic to the Sonoran Desert and serves as a crucial habitat for various wildlife. The longevity and size of this giant demonstrate the unique adaptations that cacti have developed in response to their environment.
Exploring more obscure genera, one encounters the genus Echinocactus, notable for its barrel-shaped form. Echinocacti often exhibit prominent ribbing and are adorned with a crown of spines. One particularly interesting species is Echinocactus grusonii, often referred to as the golden barrel cactus, which is recognizable for its distinct yellow spines and rounded growth form. These plants thrive in arid regions and are a testament to the extraordinary diversity within the cactus family.
Another interesting genus worth mentioning is Ferocactus. These cacti are often referred to as “fishhook cacti” due to their distinctive hooked spines. Ferocactus species can be found in the deserts of North America and are characterized by their robust growth, dramatic spines, and vibrant flowers that bloom during the summer months. A well-known example is Ferocactus wislizeni, commonly known as the southwest barrel cactus. Its resilience and striking morphology make it a popular choice among cactus enthusiasts.
Understanding cactus nomenclature also extends beyond their genus and species. The classification can be further refined by including subspecies and varieties, which denote specific adaptations or characteristics that distinguish them from their counterparts. This precision in classification helps researchers and hobbyists communicate effectively about specific plants, ensuring clarity in discussions about cactus care, conservation, and ecological roles.
Moreover, the vernacular names of cacti often differ significantly from their scientific nomenclature. Common names may represent regional dialects or cultural references, which can create confusion. Therefore, relying on the scientific name is paramount for accurate identification and discussion among botanists and enthusiasts. It allows for a standard reference point that transcends linguistic barriers.
As we explore the diversity in cactus classification, it becomes evident that understanding scientific names plays an integral role in appreciating the diversity of these remarkable plants. Beyond the aesthetic appeal and ecological importance, cacti are a source of intrigue, prompting an exploration into their evolutionary adaptations, cultivation methods, and environmental impact.
Conservation efforts in preserving native cactus species are more important now than ever. Many cacti are threatened by habitat loss, climate change, and illegal collection. By engaging in a deeper understanding of cactus taxonomy and the significance of their scientific names, we can better advocate for the preservation of these remarkable plants and the ecosystems they inhabit.
In conclusion, the world of cacti is rich and complex, encompassing various genera and species, each with its own unique adaptations and ecological roles. The scientific nomenclature not only provides clarity but also enhances our appreciation for these extraordinary plants. With further exploration and understanding, enthusiasts and scientists alike can contribute to the conservation and appreciation of cacti, ensuring their survival for future generations.



Leave a Comment